Beginners Guide: Blockchain, Bitcoin, and Breaking-In!
Hello and welcome back to Bits N’ Bytes Cybersecurity Education! This week, we are so excited to feature the voice of a growing expert in Blockchain technology, speaking about the impacts of Blockchain on the future of Cybersecurity. You have probably heard of Blockchain, and if not, you have definitely heard of Bitcoin. Over the past 9 years, the online cryptocurrency that runs completely on peer-to-peer authorizations, ridding the latency of passing through an intermediary party. BUT, what many people do not completely understand is the technology that Bitcoin runs on: Blockchain! A lot of how Blockchain works is based on past Cyber-topics we have covered including anonymity, encryption, and hashing. In today’s post, by a fellow YOUTH entrepreneur powering through and conquering this era of technology, we dive into what Blockchain is, how it is seen in our lives everyday, and how in the world does it relate to our future in Cybersecurity (even though I say it relates to everything). I bring you…the brilliant world of Blockchain technology!
What Is Blockchain And How Does It Impact Cybersecurity?
What in the HelloWorld is Blockchain?
Blockchain technology, through its decentralized and shared structure, has the potential to revolutionize cybersecurity.
Blockchain is a trending topic that has been making headlines almost everywhere over the past few years. Yet, very few people clearly understand what blockchain is and often confuse it with Bitcoin, which is just a tiny application of this technology.
The best way I like to explain blockchain is by comparing it to the current traditional monetary transactions. Let’s say you study abroad and your parents need to send you $10,000 so that you can pay for your school fees. The current banking system requires your parents to ask their bank to wire the $10,000 to you or the school where your study. The bank then virtually sends the money by subtracting the $10,000 from your parents’ bank account and adding it to yours. While there is little to no costs involved in such a transaction, the bank still charges your parents an enormous transaction fee just because it holds a central power required for the transaction to happen (in this case, the bank is the intermediary that can ensure that your money has been sent safely).
Source: Jon Phillips, Flickr
Imagine the same transaction using blockchain. In blockchain, transactions, agreements and contracts are safely recorded as a continuously growing list of records, known as blocks. This blocks keep track of the history of transactions and are able to verify a transaction without the need for a centralized system. Therefore, your parents can now send you the $10,000 with minimal transaction fees since they don’t have to rely on the bank to verify the transaction. The process also takes a few minutes/seconds as opposed to sometimes a week with banks.
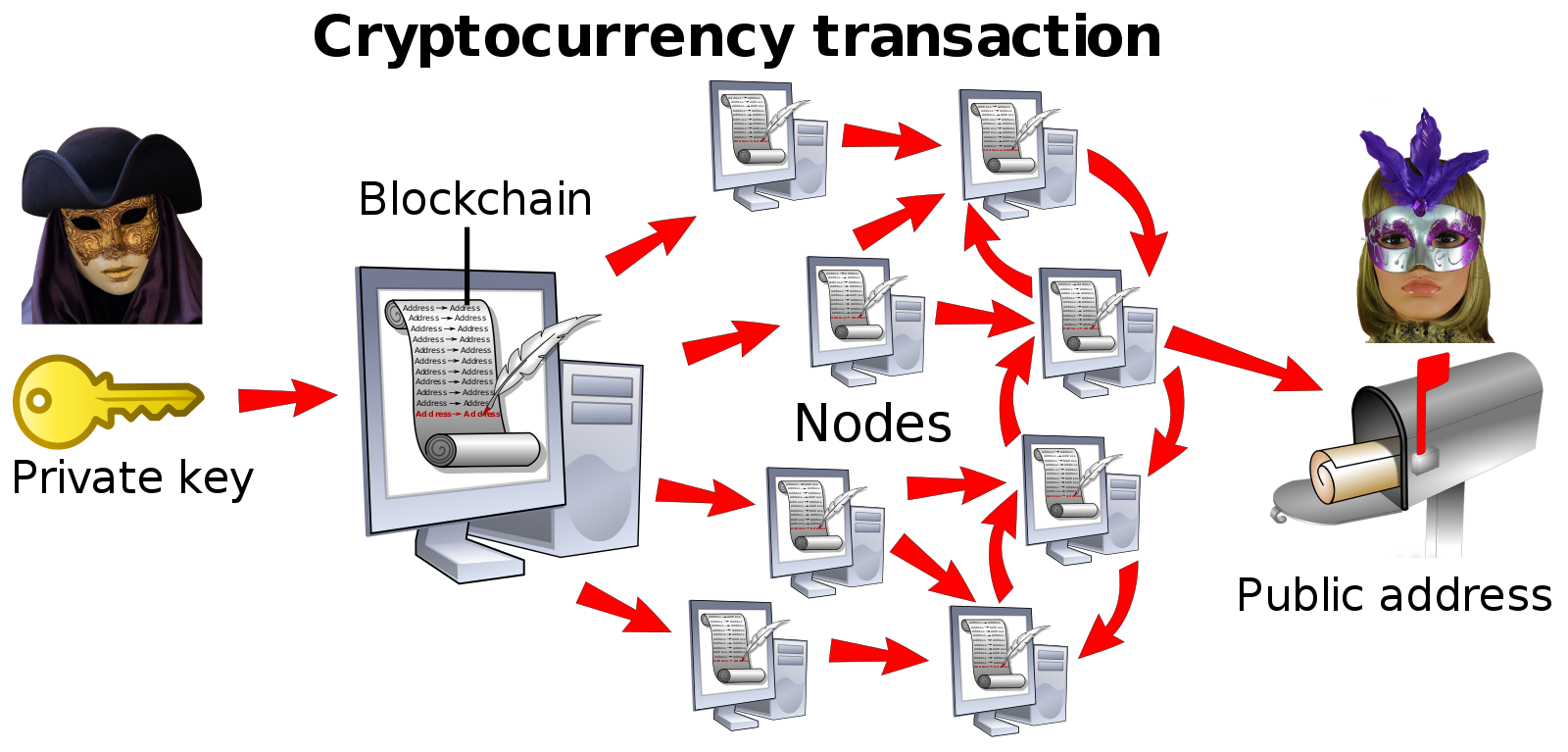
Cryptocurrency uses Blockchain’s distributed network process to facilitate transactions. Image Source: Wikipedia Commons
How does Cybersecurity relate to Blockchain?
Now that we understand blockchain and how it can be useful in monetary transactions, how is this decentralized technology relevant to cybersecurity?
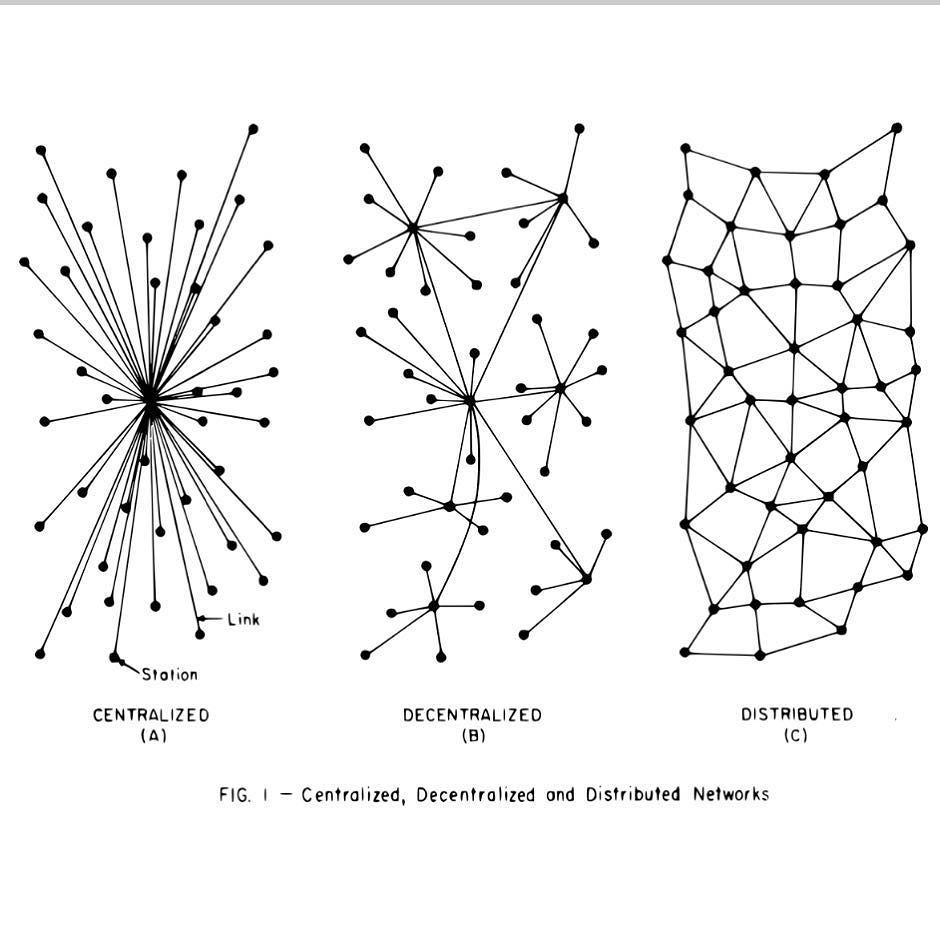
The objectives behind the research and development in blockchain technology align greatly with the principles of cybersecurity: computers use cryptography, which includes the processes of encrypting and encoding data into indecipherable forms, in order to ensure trust, security and confidentiality in communication over the Internet. Using this concept of cryptography, Blockchain is able to detect and reject fraudulent activities through its complex data encryption and auditability capabilities (using digital signatures) that ensure no point of failure through each transaction. Most importantly, the power of blockchain relies on its decentralized and distributed database structure. As explained before, data in blockchain is stored and recorded in small blocks which form a shared distributed database network. In traditional storage (aka not Blockchain), all the information is stored in one large central database, making it easier for cyber pirates to hack into the database and steal the entire payload of information or even control the system. With blockchain, however, no central body owns this information; but rather the information is shared among all the nodes within the network. As such, blockchain prevents the system from having any all-in-one hackable entrance as the hacker would need to hack all the nodes in order to reach the information.
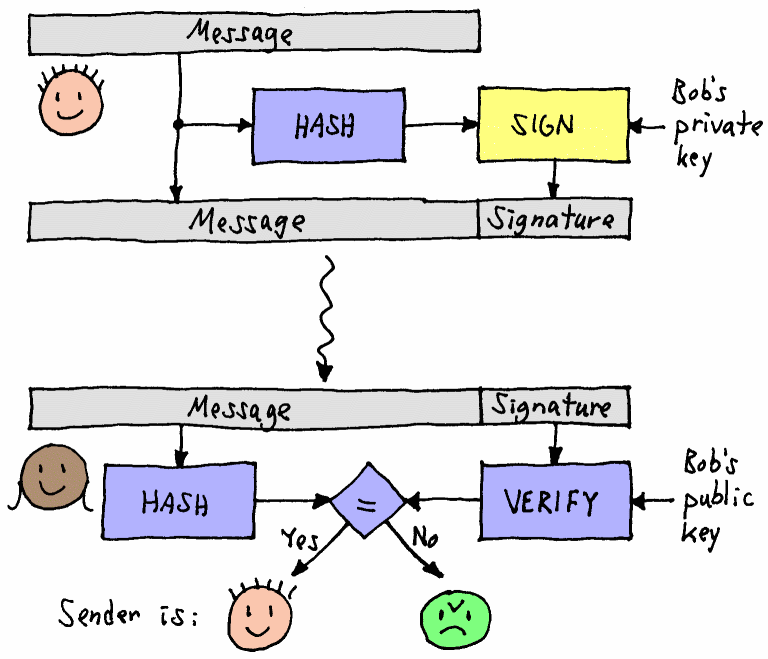
Blockchain uses digital signatures, which use cryptographic hashing, in order to ensure that no fraudulent transactions are made. Image Source: RIT CS Department
While Blockchain clearly improves cybersecurity, it has its share of limitations too. One of the biggest limitations of blockchain is its adaptability challenges to the current technical environment. It can be quite tough to implement blockchain because it requires companies and organizations to replace their existing systems which may take a substantial amount of time. Another disadvantage that comes with blockchain is the fact that any encrypted data is irreversible and and unrecoverable, with a risk of being lost in case the user fails to remember the code (or what is known as private key) required for its decryption.
So, am I using Blockchain right now?
Many startup companies have been exploring the potential impacts blockchain can have on cybersecurity. One example of this can be seen with Edge Security, a cyber-security company that claims to give individuals control of their own online data by initially encrypting their information before uploading it to a server or network. This way, all information is safely secured before uploaded making a much safer option compared to other centralized clouds such as Google Drive. Another example is Obsidian Secure Messenger (OSM), a company that uses blockchain to keep private information secure and confidential while chatting and messaging using social media. OSM doesn’t require the user to provide any Personally Identifiable Information (such as email/phone number), and it applies end-to-end encryption which ensures total protection against middle-ware attacks.
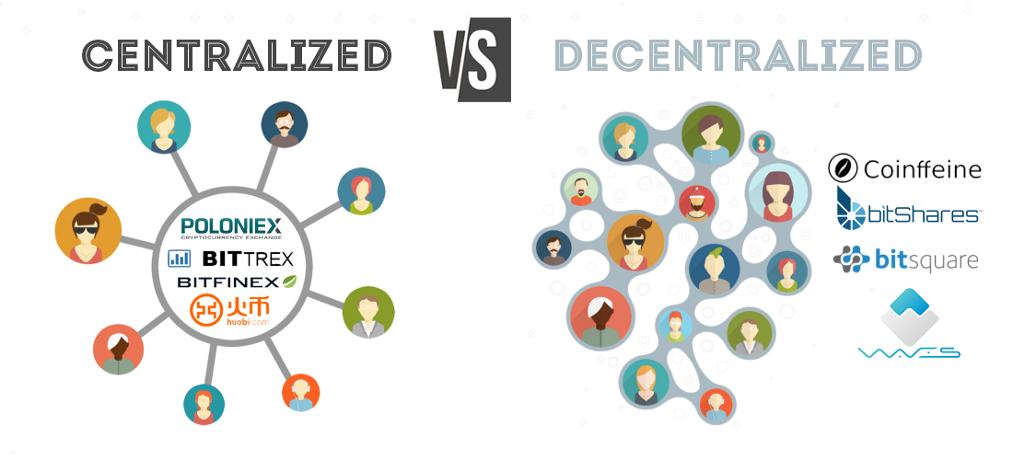
A visual of the difference between centralized and decentralized databases. Image Source: A1 Cryptobook
Blockchain clearly has the potential to advance cyber-security past borders we have seen thus far. Yet, there is still a long way to go before we can confidently say that substantial impact has been made. Blockchain still faces many challenges that hinder its progress, including adaptability issues and large operational costs and energy consumption due to the high computing power needed. In all honesty, only time can tell how great of an impact blockchain will have on cyber-security.
This post was prepared and accomplished by Mr. Amine Soufaih in his personal capacity. The opinions expressed in this article are the author’s own and do not reflect the view of any specific organization.
About the Author: Amine Soufaih
 Amine Soufaih is a young Moroccan entrepreneur and student at the African Leadership Academy (ALA). His passion lies in the intersection technology, entrepreneurship, and business. He is the co-founder and Chief Operations Officer of African Blockchain Initiative, a leading ed-tech startup specialized in Blockchain and cryptocurrency education in the African continent. Given his entrepreneurial experience, Amine was invited to speak at Harvard University and Oxford University, and was selected as a Global Teen Leader by the “We are a Family Foundation”. This upcoming fall, Amine will join the Wharton School Class of 2022 to study both business and engineering as part of the Jerome Fisher dual-degree Program.
Amine Soufaih is a young Moroccan entrepreneur and student at the African Leadership Academy (ALA). His passion lies in the intersection technology, entrepreneurship, and business. He is the co-founder and Chief Operations Officer of African Blockchain Initiative, a leading ed-tech startup specialized in Blockchain and cryptocurrency education in the African continent. Given his entrepreneurial experience, Amine was invited to speak at Harvard University and Oxford University, and was selected as a Global Teen Leader by the “We are a Family Foundation”. This upcoming fall, Amine will join the Wharton School Class of 2022 to study both business and engineering as part of the Jerome Fisher dual-degree Program.


